문서를 불러오는 중...
Spring Framework Reference Documentation 7.0.2의 Marshalling XML by Using Object-XML Mappers의 한국어 번역본입니다.
아래의 경우에 피드백에서 신고해주신다면 반영하겠습니다.
감사합니다 :)
이 장에서는 Spring의 Object-XML Mapping 지원에 대해 설명합니다. Object-XML Mapping(줄여서 O-X mapping)은 XML 문서를 객체로 그리고 객체에서 XML 문서로 변환하는 행위입니다. 이 변환 과정은 XML Marshalling 또는 XML Serialization이라고도 알려져 있습니다. 이 장에서는 이러한 용어를 서로 바꾸어 사용합니다.
O-X mapping 분야에서 marshaller는 객체(graph)를 XML로 직렬화하는 역할을 담당합니다. 마찬가지로 unmarshaller는 XML을 객체 graph로 역직렬화합니다. 이 XML은 DOM 문서, 입력 또는 출력 스트림, 혹은 SAX handler 형태를 취할 수 있습니다.
O/X mapping 요구 사항에 Spring을 사용하는 이점은 다음과 같습니다:
Spring의 bean factory는 JAXB context, JiBX binding factories 등을 구성할 필요 없이 marshaller를 쉽게 구성할 수 있게 해줍니다. 애플리케이션 컨텍스트에서 다른 bean을 구성하듯 marshaller를 구성할 수 있습니다.
추가로, 다수의 marshaller에 대해 XML namespace 기반 설정을 사용할 수 있어 구성이 더욱 간단해집니다.
Spring의 O-X mapping은 두 개의 전역 인터페이스인 Marshaller와
Unmarshaller를 통해 동작합니다. 이러한 추상화를 사용하면
marshalling을 수행하는 클래스에 거의 또는 전혀 변경을 가하지 않고도 O-X mapping 프레임워크를
상대적으로 쉽게 교체할 수 있습니다.
이 접근 방식은 추가적으로 XML marshalling을 비침투적인 방식으로 mix-and-match 방식(예를 들어, 일부 marshalling은 JAXB를 사용하고 일부는 XStream을 사용함)으로 수행할 수 있게 해주어 각 기술의 강점을 활용할 수 있게 해줍니다.
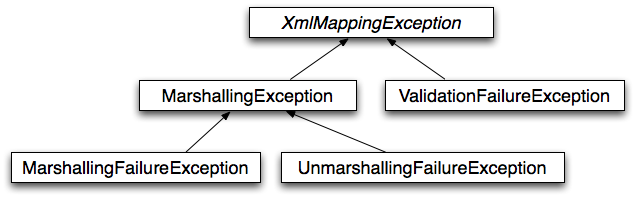
Spring은 기반 O-X mapping 도구에서 발생하는 예외를 자체 예외 계층 구조로 변환하며,
그 루트 예외는 XmlMappingException입니다.
이러한 런타임 예외는 원래 예외를 wrapping하여 어떠한 정보도 손실되지 않도록 합니다.
Marshaller and UnmarshallerIntroduction에서 언급했듯이, marshaller는 객체를 XML로 직렬화하고, unmarshaller는 XML 스트림을 객체로 역직렬화합니다. 이 섹션에서는 이 목적을 위해 사용되는 두 개의 Spring 인터페이스를 설명합니다.
MarshallerSpring은 모든 marshalling 작업을
org.springframework.oxm.Marshaller 인터페이스 뒤로 추상화하며, 그 주요 메서드는 다음과 같습니다:
1public interface Marshaller { 2 3 /** 4 * Marshal the object graph with the given root into the provided Result. 5 */ 6 void marshal(Object graph, Result result) throws XmlMappingException, IOException; 7}
Marshaller 인터페이스에는 주된 메서드가 하나 있으며, 이 메서드는 주어진 객체를
주어진 javax.xml.transform.Result로 marshal합니다. Result는 기본적으로
XML 출력 추상화를 나타내는 tagging 인터페이스입니다. 구체적인 구현체는 다음 표에서 보듯이
다양한 XML 표현을 wrapping합니다:
| Result implementation | Wraps XML representation |
|---|---|
DOMResult | org.w3c.dom.Node |
SAXResult | org.xml.sax.ContentHandler |
StreamResult | java.io.File, java.io.OutputStream, or java.io.Writer |
비록
marshal()메서드가 첫 번째 매개변수로 일반 객체를 받긴 하지만, 대부분의Marshaller구현체는 임의의 객체를 처리할 수 없습니다. 대신 객체 클래스는 매핑 파일에 매핑되어야 하거나, 어노테이션으로 표시되어야 하거나, marshaller에 등록되어야 하거나, 공통 base 클래스를 가져야 합니다. 사용 중인 O-X 기술이 이를 어떻게 관리하는지에 대해서는 이 장의 뒷부분을 참고하십시오.
UnmarshallerMarshaller와 유사하게, 다음 listing에 나오는 org.springframework.oxm.Unmarshaller
인터페이스가 있습니다:
1public interface Unmarshaller { 2 3 /** 4 * Unmarshal the given provided Source into an object graph. 5 */ 6 Object unmarshal(Source source) throws XmlMappingException, IOException; 7}
이 인터페이스 역시 하나의 메서드를 가지며,
javax.xml.transform.Source(XML 입력 추상화)에서 읽어 들여 읽은 객체를 반환합니다.
Result와 마찬가지로, Source는 세 개의 구체 구현체를 가진 tagging 인터페이스입니다. 각각은
다음 표에서 보듯이 서로 다른 XML 표현을 wrapping합니다:
| Source implementation | Wraps XML representation |
|---|---|
DOMSource | org.w3c.dom.Node |
SAXSource | org.xml.sax.InputSource, and org.xml.sax.XMLReader |
StreamSource | java.io.File, java.io.InputStream, or java.io.Reader |
두 개의 별도 marshalling 인터페이스(Marshaller와
Unmarshaller)가 존재하지만, Spring-WS의 모든 구현체는 둘 다를 하나의 클래스에서 구현합니다.
이는 하나의 marshaller 클래스를 wiring하여 applicationContext.xml에서
marshaller와 unmarshaller 둘 다로 참조할 수 있음을 의미합니다.
XmlMappingExceptionSpring은 기반 O-X mapping 도구에서 발생하는 예외를 자체 예외
계층 구조로 변환하며, 그 루트 예외는 XmlMappingException입니다.
이러한 런타임 예외는 원래 예외를 wrapping하여 어떠한 정보도 손실되지 않도록 합니다.
추가로, MarshallingFailureException과 UnmarshallingFailureException은
기반 O-X mapping 도구가 이를 구분하지 않더라도 marshalling과 unmarshalling 작업 간의
구분을 제공합니다.
O-X Mapping 예외 계층 구조는 다음 그림과 같습니다:
Marshaller and UnmarshallerSpring의 OXM은 매우 다양한 상황에서 사용할 수 있습니다. 다음 예제에서는 Spring이 관리하는 애플리케이션의 설정을 XML 파일로 marshal하는 데 이를 사용합니다. 다음 예제에서는 간단한 JavaBean을 사용하여 설정을 표현합니다:
1public class Settings { 2 3 private boolean fooEnabled; 4 5 public boolean isFooEnabled() { 6 return fooEnabled; 7 } 8 9 public void setFooEnabled(boolean fooEnabled) { 10 this.fooEnabled = fooEnabled; 11 } 12}
1class Settings { 2 var isFooEnabled: Boolean = false 3}
애플리케이션 클래스는 이 bean을 사용하여 설정을 저장합니다. main 메서드 외에도,
이 클래스에는 두 개의 메서드가 있습니다: saveSettings()는 settings bean을
settings.xml이라는 이름의 파일에 저장하고, loadSettings()는 이 설정을 다시 로드합니다.
다음 main() 메서드는
Spring 애플리케이션 컨텍스트를 구성하고 이 두 메서드를 호출합니다:
1import java.io.FileInputStream; 2import java.io.FileOutputStream; 3import java.io.IOException; 4import javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamResult; 5import javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamSource; 6import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 7import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 8import org.springframework.oxm.Marshaller; 9import org.springframework.oxm.Unmarshaller; 10 11public class Application { 12 13 private static final String FILE_NAME = "settings.xml"; 14 private Settings settings = new Settings(); 15 private Marshaller marshaller; 16 private Unmarshaller unmarshaller; 17 18 public void setMarshaller(Marshaller marshaller) { 19 this.marshaller = marshaller; 20 } 21 22 public void setUnmarshaller(Unmarshaller unmarshaller) { 23 this.unmarshaller = unmarshaller; 24 } 25 26 public void saveSettings() throws IOException { 27 try (FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(FILE_NAME)) { 28 this.marshaller.marshal(settings, new StreamResult(os)); 29 } 30 } 31 32 public void loadSettings() throws IOException { 33 try (FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(FILE_NAME)) { 34 this.settings = (Settings) this.unmarshaller.unmarshal(new StreamSource(is)); 35 } 36 } 37 38 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 39 ApplicationContext appContext = 40 new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 41 Application application = (Application) appContext.getBean("application"); 42 application.saveSettings(); 43 application.loadSettings(); 44 } 45}
1class Application { 2 3 lateinit var marshaller: Marshaller 4 5 lateinit var unmarshaller: Unmarshaller 6 7 fun saveSettings() { 8 FileOutputStream(FILE_NAME).use { outputStream -> marshaller.marshal(settings, StreamResult(outputStream)) } 9 } 10 11 fun loadSettings() { 12 FileInputStream(FILE_NAME).use { inputStream -> settings = unmarshaller.unmarshal(StreamSource(inputStream)) as Settings } 13 } 14} 15 16private const val FILE_NAME = "settings.xml" 17 18fun main(args: Array<String>) { 19 val appContext = ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml") 20 val application = appContext.getBean("application") as Application 21 application.saveSettings() 22 application.loadSettings() 23}
Application은 marshaller와 unmarshaller 프로퍼티가 둘 다 설정되어야 합니다.
다음 applicationContext.xml을 사용하여 이를 설정할 수 있습니다:
1<beans> 2 <bean id="application" class="Application"> 3 <property name="marshaller" ref="xstreamMarshaller" /> 4 <property name="unmarshaller" ref="xstreamMarshaller" /> 5 </bean> 6 <bean id="xstreamMarshaller" class="org.springframework.oxm.xstream.XStreamMarshaller"/> 7</beans>
이 애플리케이션 컨텍스트는 XStream을 사용하지만, 이 장의 뒷부분에서 설명하는 다른 marshaller 인스턴스를 사용할 수도 있습니다. 기본적으로 XStream은 추가 구성을 필요로 하지 않으므로 bean 정의는 상당히 단순합니다.
또한 XStreamMarshaller는 Marshaller와 Unmarshaller 모두를
구현하므로, 애플리케이션의 marshaller 및 unmarshaller 프로퍼티에서
xstreamMarshaller bean을 참조할 수 있습니다.
이 샘플 애플리케이션은 다음과 같은 settings.xml 파일을 생성합니다:
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2<settings foo-enabled="false"/>
OXM namespace의 태그를 사용하면 marshaller를 더 간결하게 구성할 수 있습니다. 이러한 태그를 사용 가능하게 만들기 위해서는 먼저 XML 설정 파일의 preamble에서 적절한 스키마를 참조해야 합니다. 다음 예제는 그 방법을 보여줍니다:
1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:oxm="http://www.springframework.org/schema/oxm" (1) 5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 6 https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/oxm 8 https://www.springframework.org/schema/oxm/spring-oxm.xsd"> (2)
1
oxm스키마를 참조합니다. 2oxm스키마 위치를 지정합니다.
이 스키마는 다음 element를 사용할 수 있게 합니다:
각 태그는 해당 marshaller 섹션에서 설명됩니다. 예를 들어, JAXB2 marshaller의 설정은 다음과 비슷할 수 있습니다:
1<oxm:jaxb2-marshaller id="marshaller" contextPath="org.springframework.ws.samples.airline.schema"/>
JAXB binding 컴파일러는 W3C XML 스키마를 하나 이상의 Java 클래스,
jaxb.properties 파일, 그리고 일부 리소스 파일로 변환합니다. JAXB는 또한
어노테이션이 달린 Java 클래스에서 스키마를 생성하는 방법도 제공합니다.
Spring은 XML marshalling 전략으로 JAXB 2.0 API를 지원하며,
Marshaller and Unmarshaller에서 설명한
Marshaller 및 Unmarshaller 인터페이스를 따릅니다.
해당 integration 클래스는 org.springframework.oxm.jaxb
패키지에 위치합니다.
Jaxb2MarshallerJaxb2Marshaller 클래스는 Spring의 Marshaller와 Unmarshaller
인터페이스를 모두 구현합니다. 동작하기 위해 context path가 필요합니다. context path는
contextPath 프로퍼티를 설정하여 지정할 수 있습니다. context path는 스키마에서 파생된 클래스를 포함하는
Java 패키지 이름을 콜론으로 구분한 목록입니다.
또한 marshaller에서 지원할
클래스 배열을 설정할 수 있는 classesToBeBound 프로퍼티도 제공합니다. 스키마
검증은 다음 예제에서 보듯이 bean에 하나 이상의 스키마 리소스를 지정함으로써 수행됩니다:
1<beans> 2 <bean id="jaxb2Marshaller" class="org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Jaxb2Marshaller"> 3 <property name="classesToBeBound"> 4 <list> 5 <value>org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Flight</value> 6 <value>org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Flights</value> 7 </list> 8 </property> 9 <property name="schema" value="classpath:org/springframework/oxm/schema.xsd"/> 10 </bean> 11 12 ... 13 14</beans>
jaxb2-marshaller element는 org.springframework.oxm.jaxb.Jaxb2Marshaller를
구성하며, 다음 예제와 같습니다:
1<oxm:jaxb2-marshaller id="marshaller" contextPath="org.springframework.ws.samples.airline.schema"/>
또는, class-to-be-bound child element를 사용하여 marshaller에 binding할
클래스 목록을 제공할 수 있습니다:
1<oxm:jaxb2-marshaller id="marshaller"> 2 <oxm:class-to-be-bound name="org.springframework.ws.samples.airline.schema.Airport"/> 3 <oxm:class-to-be-bound name="org.springframework.ws.samples.airline.schema.Flight"/> 4 ... 5</oxm:jaxb2-marshaller>
다음 표는 사용 가능한 attribute를 설명합니다:
| Attribute | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
id | marshaller의 ID | No |
contextPath | JAXB Context path | No |
JiBX 프레임워크는 ORM에 대해 Hibernate가 제공하는 것과 유사한 해결책을 제공합니다: binding 정의는 Java 객체가 XML로부터 또는 XML로 어떻게 변환되는지에 대한 규칙을 정의합니다. binding을 준비하고 클래스를 컴파일한 후 JiBX binding 컴파일러는 클래스 파일을 확장하고 인스턴스를 XML로부터 또는 XML로 변환하는 코드를 추가합니다.
JiBX에 대한 자세한 내용은 JiBX web
site를 참조하십시오. Spring integration 클래스는 org.springframework.oxm.jibx
패키지에 위치합니다.
JibxMarshallerJibxMarshaller 클래스는 Marshaller와 Unmarshaller
인터페이스를 모두 구현합니다. 동작하기 위해 marshal할 클래스 이름이 필요하며,
이는 targetClass 프로퍼티를 사용하여 설정할 수 있습니다. 선택적으로,
bindingName 프로퍼티를 설정하여 binding 이름을 지정할 수 있습니다.
다음 예제에서는 Flights 클래스를 binding합니다:
1<beans> 2 <bean id="jibxFlightsMarshaller" class="org.springframework.oxm.jibx.JibxMarshaller"> 3 <property name="targetClass">org.springframework.oxm.jibx.Flights</property> 4 </bean> 5 ... 6</beans>
JibxMarshaller는 단일 클래스에 대해 구성됩니다. 여러
클래스를 marshal하려면, 서로 다른 targetClass
프로퍼티 값을 가진 여러 JibxMarshaller 인스턴스를 구성해야 합니다.
jibx-marshaller 태그는 org.springframework.oxm.jibx.JibxMarshaller를
구성하며, 다음 예제와 같습니다:
1<oxm:jibx-marshaller id="marshaller" target-class="org.springframework.ws.samples.airline.schema.Flight"/>
다음 표는 사용 가능한 attribute를 설명합니다:
| Attribute | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
id | marshaller의 ID | No |
target-class | 이 marshaller의 target 클래스 | Yes |
bindingName | 이 marshaller에서 사용하는 binding 이름 | No |
XStream은 객체를 XML로 직렬화하고 다시 되돌리는 단순한 라이브러리입니다. 어떠한 매핑도 필요로 하지 않으며 깔끔한 XML을 생성합니다.
XStream에 대한 자세한 내용은 XStream
web site를 참조하십시오. Spring integration 클래스는
org.springframework.oxm.xstream 패키지에 위치합니다.
XStreamMarshallerXStreamMarshaller는 어떠한 설정도 필요로 하지 않으며
애플리케이션 컨텍스트에서 바로 구성할 수 있습니다. XML을 더 세밀하게 커스터마이즈하기 위해
문자열 alias를 클래스에 매핑한 alias 맵을 설정할 수 있으며, 다음 예제와 같습니다:
1<beans> 2 <bean id="xstreamMarshaller" class="org.springframework.oxm.xstream.XStreamMarshaller"> 3 <property name="aliases"> 4 <props> 5 <prop key="Flight">org.springframework.oxm.xstream.Flight</prop> 6 </props> 7 </property> 8 </bean> 9 ... 10</beans>
기본적으로 XStream은 임의의 클래스가 unmarshalled되도록 허용하며, 이는 안전하지 않은 Java serialization 효과를 초래할 수 있습니다. 따라서,
XStreamMarshaller를 사용하여 외부 소스(즉, Web)에서 온 XML을 unmarshal하는 것은 보안 취약점을 초래할 수 있으므로 권장하지 않습니다. 외부 소스에서 온 XML을 unmarshal하기 위해XStreamMarshaller를 사용하기로 선택한 경우, 다음 예제와 같이XStreamMarshaller에서supportedClasses프로퍼티를 설정하십시오:1<bean id="xstreamMarshaller" class="org.springframework.oxm.xstream.XStreamMarshaller"> 2 <property name="supportedClasses" value="org.springframework.oxm.xstream.Flight"/> 3 ... 4</bean>이렇게 하면 등록된 클래스만 unmarshalling 대상이 되도록 보장합니다. 추가로, custom converters를 등록하여 지원되는 클래스만 unmarshalled되도록 할 수 있습니다. 또한 지원되어야 하는 도메인 클래스를 명시적으로 지원하는 converter 외에, 리스트의 마지막 converter로
CatchAllConverter를 추가하고 싶을 수 있습니다. 그 결과, 우선순위가 낮고 잠재적인 보안 취약점을 가진 기본 XStream converter는 호출되지 않습니다.
XStream은 data binding 라이브러리가 아니라 XML serialization 라이브러리라는 점에 유의하십시오. 따라서 제한적인 namespace 지원을 제공합니다. 그 결과 Web Services 내에서 사용하기에는 상당히 부적합합니다.
JPA
Appendix